What Changes Are Seen In Our Body's Water Balance As We Get Older?
The trunk changes with crumbling because changes occur in private cells and in whole organs. These changes result in changes in function and in appearance.
As cells age, they office less well. Eventually, sometime cells must die, which is a normal part of the body's performance.
Old cells sometimes dice because they are programmed to exercise so. The genes of cells plan a process that, when triggered, results in expiry of the prison cell. This programmed death, called apoptosis, is a kind of cell suicide. The aging of a cell is one trigger. Erstwhile cells must die to make room for new cells. Other triggers include an backlog number of cells and mayhap damage to a cell.
One-time cells likewise dice considering they tin divide simply a limited number of times. This limit is programmed by genes. When a cell can no longer divide, it grows larger, exists for a while, then dies. The mechanism that limits cell division involves a structure called a telomere. Telomeres are used to move the cell's genetic material in preparation for cell division. Every time a cell divides, the telomeres shorten a bit. Eventually, the telomeres get so brusque that the cell can no longer split. When a jail cell stops dividing, information technology is called senescence.
Sometimes damage to a cell directly causes its death. Cells may exist damaged past harmful substances, such every bit radiation, sunlight, and chemotherapy drugs. Cells may besides be damaged by certain by-products of their own normal activities. These past-products, chosen gratis radicals, are given off when cells produce energy.
How well organs function depends on how well the cells within them function. Older cells role less well. Too, in some organs, cells dice and are non replaced, and so the number of cells decreases. The number of cells in the testes, ovaries, liver, and kidneys decreases markedly every bit the body ages. When the number of cells becomes too low, an organ cannot function commonly. Thus, nigh organs function less well every bit people age. Withal, non all organs lose a large number of cells. The brain is 1 example. Good for you older people do not lose many brain cells. Substantial losses occur mainly in people who accept had a stroke Overview of Stroke A stroke occurs when an avenue to the encephalon becomes blocked or ruptures, resulting in decease of an area of brain tissue due to loss of its blood supply (cerebral infarction) and symptoms that... read more or who have a disorder that causes the progressive loss of nervus cells (neurodegenerative disorders), such as Alzheimer illness Alzheimer Disease Alzheimer illness is a progressive loss of mental function, characterized by degeneration of brain tissue, including loss of nerve cells, the accumulation of an abnormal protein called beta-amyloid... read more or Parkinson disease Parkinson Disease (PD) Parkinson disease is a slowly progressive degenerative disorder of specific areas of the brain. It is characterized past tremor when muscles are at rest (resting tremor), increased musculus tone... read more .
Often, the get-go signs of aging involve the musculoskeletal system. The eyes, followed by the ears, brainstorm to alter early in mid-life. Well-nigh internal functions also decline with crumbling. Almost bodily functions peak soon before age xxx and and so begin a gradual but continuous decline. However, even with this reject, most functions remain adequate considering near organs first with considerably more functional chapters than the body needs (functional reserve). For example, if half the liver is destroyed, the remaining tissue is more enough to maintain normal function. Thus, disorders, rather than normal crumbling, usually business relationship for most of the loss of part in onetime historic period.
Even though most functions remain adequate, the refuse in function means that older people are less able to handle various stresses, including strenuous physical activity, extreme temperature changes in the surround, and disorders. This decline also means that older people are more than likely to experience side effects from drugs. Some organs are more probable to malfunction under stress than others. These organs include the heart and blood vessels, the urinary organs (such as the kidneys), and the brain.
Bones go less dense partly because they contain less calcium (which gives bones strength). The amount of calcium decreases because the body absorbs less calcium from foods. Also, levels of vitamin D, which helps the torso apply calcium, decrease slightly. Certain basic are weakened more than than others. Those near affected include the end of the thighbone (femur) at the hip, the ends of the arm bones (radius and ulna) at the wrist, and the basic of the spine (vertebrae).
Changes in vertebrae at the tiptop of the spine cause the head to tip forrad, compressing the throat. As a upshot, swallowing is more hard, and choking is more likely. The vertebrae become less dense and the cushions of tissue (disks) between them lose fluid and become thinner, making the spine shorter. Thus, older people go shorter.
Ligaments, which demark joints together, and tendons, which bind muscle to bone, tend to get less elastic, making joints feel tight or stiff. These tissues too weaken. Thus, most people become less flexible. Ligaments and tendons tend to tear more than hands, and when they tear, they heal more slowly. These changes occur because the cells that maintain ligaments and tendons become less active.
The corporeality of musculus tissue (muscle mass) and muscle strength tend to decrease offset around historic period thirty and standing throughout life. Some of the decrease is caused by physical inactivity and decreasing levels of growth hormone and testosterone , which stimulate muscle evolution. Also, muscles cannot contract as quickly because more fast-contracting (fast-twitch) muscle fibers are lost than irksome-contracting (slow-twitch) muscle fibers. Notwithstanding, aging'southward effects reduce musculus mass and strength by no more than near ten to 15% during an adult'southward lifetime. In the absence of disease, nearly of the loss beyond that ten to 15% is preventable with regular exercise. More than severe muscle loss (chosen sarcopenia, which literally means loss of flesh) results from disease or extreme inactivity, non from aging lone.
Most older people retain enough muscle mass and forcefulness for all necessary tasks. Many older people remain stiff athletes. They compete in sports and enjoy vigorous concrete activity. However, even the fittest notice some decline equally they age.
Regular exercise Exercise in Older Adults At least 75% of people over historic period 65 exercise not exercise at recommended levels despite the known wellness benefits of practise including Longer survival Improved quality of life (for case, endurance... read more to strengthen muscles (resistance preparation) tin can partially overcome or significantly delay loss of musculus mass and forcefulness. In muscle-strengthening exercise, muscles contract against resistance provided by gravity (as in sit-ups or push button-ups), weights, or condom bands. If this type of exercise is done regularly, even people who accept never exercised tin increase muscle mass and strength. Conversely, physical inactivity, especially bed rest during an illness, tin profoundly accelerate the loss. During periods of inactivity, older people lose musculus mass and force much more quickly than younger people practice. For example, to make upward for the muscle mass lost during each day of strict bed rest, people may demand to exercise for up to 2 weeks.
By historic period 75, the percent of body fat typically doubles compared with what it was during immature adulthood. Too much body fat can increase the gamble of health problems, such equally diabetes Diabetes Mellitus (DM) and Disorders of Claret Carbohydrate Metabolism . The distribution of fat besides changes, changing the shape of the torso. A healthy diet and regular practice tin aid older people minimize increases in body fatty.
Every bit people age, the post-obit occur:
-
The lens stiffens, making focusing on shut objects harder.
-
The lens becomes denser, making seeing in dim light harder.
-
The pupil reacts more than slowly to changes in calorie-free.
-
The lens yellows, irresolute the way colors are perceived.
-
The number of nerve cells decrease, impairing depth perception.
-
The eyes produce less fluid, making them feel dry.
A modify in vision is oft the first undeniable sign of aging.
Changes in the lenses of the eye can cause or contribute to the post-obit:
-
Loss of well-nigh vision: During their 40s, well-nigh people detect that seeing objects closer than 2 feet becomes difficult. This change in vision, chosen presbyopia Causes
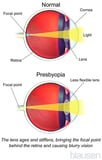 , occurs considering the lens in the eye stiffens. Normally, the lens changes its shape to help the middle focus. A stiffer lens makes focusing on shut objects harder. Ultimately, almost everyone gets presbyopia and needs magnifying reading glasses. People who need glasses to meet distant objects may need to wear bifocals or spectacles with variable-focus lenses.
, occurs considering the lens in the eye stiffens. Normally, the lens changes its shape to help the middle focus. A stiffer lens makes focusing on shut objects harder. Ultimately, almost everyone gets presbyopia and needs magnifying reading glasses. People who need glasses to meet distant objects may need to wear bifocals or spectacles with variable-focus lenses. -
Need for brighter light: As people continue to age, seeing in dim light becomes more than difficult considering the lens tends to become less transparent. A denser lens means that less calorie-free passes through to the retina at the dorsum of the eye. Too, the retina, which contains the cells that sense lite, becomes less sensitive. Then for reading, brighter light is needed. On average, 60-year-olds need 3 times more than light to read than 20-yr-olds.
-
Changes in color perception: Colors are perceived differently, partly because the lens tends to yellow with aging. Colors may wait less bright and contrasts between different colors may be more difficult to see. Dejection may look more grayness, and blue print or background may await done out. These changes are insignificant for virtually people. However, older people may have trouble reading black letters printed on a blue background or reading blue messages.
The pupil of the middle reacts more slowly to changes in light. The student widens and narrows to permit more or less calorie-free in, depending on the effulgence of the environs. A slow-reacting pupil ways that older people may be unable to see when they first enter a dark room. Or they may be temporarily blinded when they enter a brightly lit area. Older people may also get more sensitive to glare Glare and Halos A number of other symptoms and problems can touch the eyes, including changes in the appearance of the eyes, color blindness, dry optics, glare and halos, impaired depth perception, itchy eyes... read more than . However, increased sensitivity to glare is often due to darkened areas in the lens or to cataracts Cataract A cataract is a clouding (opacity) of the lens of the centre that causes a progressive, painless loss of vision. Vision may be blurred, contrast may exist lost, and halos may be visible around lights... read more 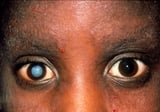 .
.
Fine details, including differences in shades and tones, become more difficult to discern. The reason is probably a subtract in the number of nerve cells that transmit visual signals from the eyes to the brain. This change affects the mode depth is perceived, and judging distances becomes more difficult.
The advent of the optics changes in several ways:
-
The whites (sclera) of the eyes may turn slightly yellow or brownish. This change results from many years of exposure to ultraviolet low-cal, current of air, and dust.
-
Random splotches of color may appear in the whites of the eyes, particularly in people with a dark complexion.
-
A gray-white ring (arcus senilis) may appear on the surface of the eye. The band is fabricated of calcium and cholesterol salts. It does not affect vision.
-
The eye may announced to sink into the caput because the corporeality of fatty effectually the middle decreases.
It is important to come across a doctor to determine whether hearing loss is due to cerumen (ear wax) impaction because this is easily treated.
As people historic period, hearing high-pitched sounds becomes more difficult. This modify is considered age-associated hearing loss (presbycusis). For instance, violin music may sound less bright.
The most frustrating consequence of presbycusis is that words go harder to sympathize. As a upshot, older people may think that other people are mumbling. Even when other people speak more than loudly, older people still accept difficulty understanding the words. The reason is that nigh consonants (such equally chiliad, t, s, p, and ch) are high-pitched, and consonants are the sounds that help people identify words. Because vowels are lower-pitched sounds, they are easier to hear. And so older people may hear "Ell me exaly wha yous wan oo ee," rather than "Tell me exactly what you want to go along." To assistance, other people need to articulate consonants more conspicuously, rather than simply speak louder. Understanding what women and children say may be more difficult than agreement what men say because most women and children have higher-pitched voices. Gradually, hearing lower pitches as well becomes more difficult.
Many older people take more trouble hearing in loud places or in groups because of the background racket.
Thick hairs may grow out of the ears.
(Run across likewise Effects of Aging on the Rima oris and Teeth Furnishings of Crumbling on the Mouth and Teeth With crumbling, taste sensation may diminish. Older people may notice their nutrient tastes bland then, for more taste, they may add together abundant seasonings (specially salt, which is harmful for some people)... read more than and Effects of Aging on the Ears, Nose, and Pharynx Effects of Aging on the Ears, Nose, and Throat Aging affects the function of the ears, nose, and pharynx in varying degrees. The furnishings of aging result from many factors such as wear and tear caused by overuse of the voice, exposure to loud... read more .)
Generally, when people are in their 50s, the power to taste and smell starts to gradually diminish. Both senses are needed to enjoy the total range of flavors in food. The tongue tin identify just five bones tastes: sugariness, sour, bitter, table salt, and a taste called umami (ordinarily described as meaty or savory). The sense of odor is needed to distinguish more subtle and complex flavors (such equally raspberry).
As people age, taste buds on the tongue decrease in sensitivity. This change affects tasting sweet and salt more than bitter and sour. The ability to smell diminishes because the lining of the nose becomes thinner and drier and the nerve endings in the olfactory organ deteriorate. However, the change is slight, usually affecting but subtle smells. Because of these changes, many foods tend to taste bitter, and foods with subtle smells may sense of taste bland.
With crumbling, the nose tends to lengthen and enlarge, and the tip tends to droop.
Thick hairs may abound in the nose and on the upper lip and chin.
The skin tends to get thinner, less elastic, drier, and finely wrinkled. However, exposure to sunlight over the years greatly contributes to wrinkling and to making the skin rough and blotchy. People who have avoided exposure to sunlight oft look much younger than their historic period.
The skin changes partly because collagen (a tough, fibrous tissue that makes pare strong) and elastin (which makes peel flexible) become chemically changed and less flexible; also, the aging trunk produces less collagen and elastin. Every bit a result, the peel tears more easily.
The fat layer under the skin thins. This layer acts as a cushion for the skin, helping protect and back up information technology. The fatty layer also helps conserve torso heat. When the layer thins, wrinkles are more likely to develop, and tolerance for cold decreases.
The number of nerve endings in the peel decreases. Equally a result, people go less sensitive to pain, temperature, and pressure, and injuries may be more likely.
The number of sweat glands and blood vessels decreases, and blood catamenia in the deep layers of the skin decreases. As a result, the body is less able to move heat from within the body through blood vessels to the surface of the torso. Less heat leaves the trunk, and the body cannot cool itself too. Thus, the take a chance of oestrus-related disorders, such equally heatstroke, is increased. Also, when blood flow is decreased, the skin tends to heal more slowly.
The number of pigment-producing cells (melanocytes) decreases. As a upshot, the skin has less protection against ultraviolet (UV) radiation, such every bit that from sunlight. Large, brown spots (age spots) develop on skin that has been exposed to sunlight, mayhap because the skin is less able to remove waste matter products.
The number of nerve cells in the encephalon typically decreases. However, the brain tin partly compensate for this loss in several ways:
-
As cells are lost, new connections are made between the remaining nervus cells.
-
New nervus cells may form in some areas of the brain, even during old age.
-
The brain has more than cells than information technology needs to practice most activities—a characteristic called redundancy.
Levels of the chemical substances involved in sending messages in the encephalon tend to decrease, merely some increase. Nervus cells may lose some of their receptors for these chemical messages. Blood flow to the brain decreases. Considering of these historic period-related changes, the brain may function slightly less well. Older people may react and practise tasks somewhat more slowly, only given time, they exercise these things accurately. Some mental functions—such equally vocabulary, short-term memory, the ability to learn new material, and the ability to recall words—may be subtly reduced later historic period 70.
After about age lx, the number of cells in the spinal cord begins to subtract. Usually, this alter does non touch on force or awareness.
As people age, fretfulness may carry signals more slowly. Usually, this change is so minimal that people practice non notice it. Too, nerves may repair themselves more than slowly and incompletely. Therefore, in older people with damaged nerves, sensation and strength may be decreased.
The heart and claret vessels become stiffer. The heart fills with blood more than slowly. The stiffer arteries are less able to expand when more blood is pumped through them. Thus, blood pressure tends to increase.
Despite these changes, a normal older heart functions well. Differences betwixt immature and old hearts become credible only when the heart has to piece of work difficult and pump more blood—for example, during exercise or an illness. An older heart cannot speed up as quickly or pump equally fast or as much blood every bit a younger center. Thus, older athletes are not able to perform every bit well as younger athletes. Withal, regular aerobic exercise can improve able-bodied performance in older people.
The muscles used in animate, the diaphragm and muscles betwixt the ribs, tend to weaken. The number of air sacs (alveoli) and capillaries in the lungs decreases. Thus, slightly less oxygen is absorbed from air that is breathed in. The lungs go less rubberband. In people who do not fume or have a lung disorder, these changes do not affect ordinary daily activities, but these changes may make exercising more difficult. Breathing at high altitudes (where at that place is less oxygen) may as well be harder.
The lungs become less able to fight infection, partly considering the cells that sweep debris containing microorganisms out of the airways are less able to exercise so. Cough, which also helps clear the lungs, tends to exist weaker.
Overall, the digestive system is less affected by crumbling than virtually other parts of the trunk. The muscles of the esophagus contract less forcefully, simply movement of food through the esophagus is non affected. Nutrient is emptied from the tummy slightly more slowly, and the stomach cannot hold as much nutrient because it is less rubberband. But in most people, these changes are likewise slight to be noticed.
The liver tends to get smaller considering the number of cells decreases. Less blood flows through it, and liver enzymes that aid the body process drugs and other substances work less efficiently. Every bit a issue, the liver may be slightly less able to assist remove drugs and other substances from the body. And the furnishings of drugs—intended and unintended—last longer.
The kidneys tend to become smaller because the number of cells decreases. Less claret flows through the kidneys, and at about historic period xxx, they begin to filter blood less well. As years laissez passer, they may remove waste products from the claret less well. They may excrete too much water and too little salt, making dehydration more probable. Nonetheless, they almost always function well enough to meet the body's needs.
Sure changes in the urinary tract may make controlling urination more than difficult:
-
The maximum book of urine that the float can hold decreases. Thus, older people may need to urinate more oftentimes.
-
The float muscles may contract unpredictably (get overactive), regardless of whether people need to urinate.
-
The bladder muscles weaken. Every bit a result, they cannot empty the bladder too, and more urine is left in the bladder later on urination.
-
The musculus that controls the passage of urine out of the torso (urinary sphincter) is less able to close tightly and prevent leakage. Thus, older people have more difficulty postponing urination.
In women, the urethra (the tube through which urine leaves the body) shortens, and its lining becomes thinner. The decrease in the estrogen level that occurs with menopause may contribute to this and other changes in the urinary tract.
The effects of aging on sex hormone levels are more obvious in women than in men. In women, most of these effects are related to menopause Menopause Menopause is the permanent end of menstrual periods and thus of fertility. For up to several years earlier and just afterwards menopause, estrogen levels fluctuate widely, periods become irregular... read more  , when the levels of female hormones (particularly estrogen) decrease dramatically, menstrual periods finish permanently, and pregnancy is no longer possible. The decrease in female hormone levels causes the ovaries and uterus to compress. The tissues of the vagina become thinner, drier, and less elastic (a condition chosen atrophic vaginitis). In severe cases, these changes can lead to itching, haemorrhage, pain during intercourse, and a need to urinate immediately (urinary urgency Urinary Urgency A compelling need to urinate (urgency), which may experience similar nearly abiding painful straining (tenesmus), can exist caused past bladder irritation. Uncontrolled loss of urine (incontinence) may occur... read more ).
, when the levels of female hormones (particularly estrogen) decrease dramatically, menstrual periods finish permanently, and pregnancy is no longer possible. The decrease in female hormone levels causes the ovaries and uterus to compress. The tissues of the vagina become thinner, drier, and less elastic (a condition chosen atrophic vaginitis). In severe cases, these changes can lead to itching, haemorrhage, pain during intercourse, and a need to urinate immediately (urinary urgency Urinary Urgency A compelling need to urinate (urgency), which may experience similar nearly abiding painful straining (tenesmus), can exist caused past bladder irritation. Uncontrolled loss of urine (incontinence) may occur... read more ).
The breasts get less firm and more fibrous, and they tend to sag. These changes make finding lumps in the breasts more difficult.
Some of the changes that begin at menopause (such as lower hormone levels and vaginal dryness) may interfere with sex. Withal, for near women, aging does not profoundly detract from enjoyment of sexual practice. Not having to worry about becoming pregnant may heighten sexual activity and enjoyment.
The levels and action of some hormones, produced by endocrine glands, decrease.
-
Growth hormone levels decrease, leading to decreased muscle mass.
-
Aldosterone levels decrease, making aridity more likely. This hormone signals the body to retain salt and therefore water.
-
Insulin, which helps control the carbohydrate (glucose) level in blood, is less effective, and less insulin may be produced. Insulin enables sugar to motility from the claret into cells, where information technology can be converted to energy. The changes in insulin mean that the sugar level increases more after a large repast and takes longer to return to normal.
-
Cancer is more common among older people.
-
Vaccines tend to exist less protective in older people, but influenza, pneumonia, and shingles vaccines are essential and offering some protection.
-
Some infections, such as pneumonia and influenza, are more common amidst older people and result in death more often.
-
Allergy symptoms may get less severe.
As the immune system slows downwardly, autoimmune disorders get less common.
Source: https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/older-people%E2%80%99s-health-issues/the-aging-body/changes-in-the-body-with-aging
Posted by: chavezhond1975.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Changes Are Seen In Our Body's Water Balance As We Get Older?"
Post a Comment